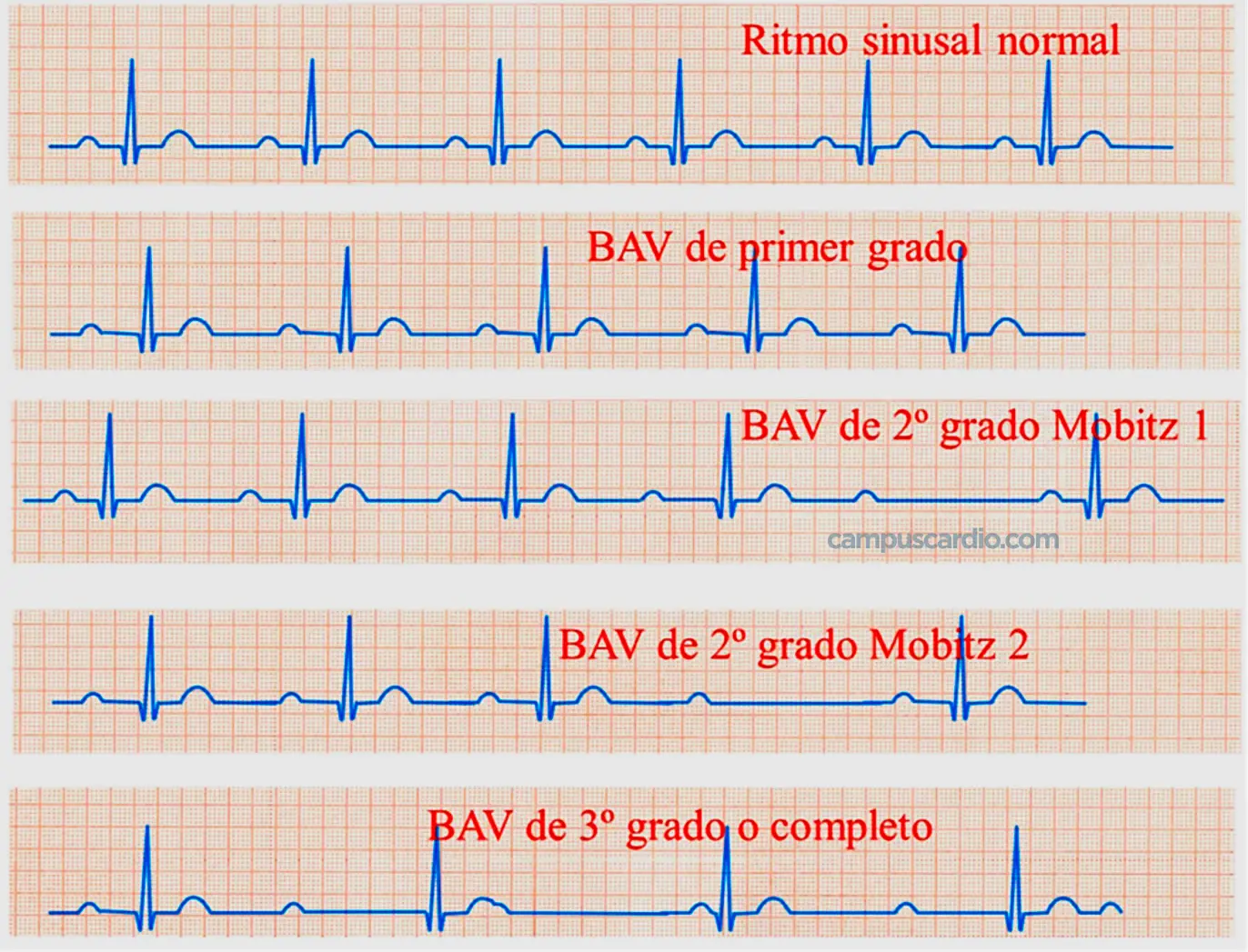
First degree: electrical conduction to the ventricles is delayed. Second degree: electrical conduction is blocked intermittently. Third degree (complete): electrical conduction is completely blocked.
First-degree heart block is a condition in which the heart’s circuitry is slow to send electrical signals. But all signals correctly pass through the heart. There is no real lock. But the signal between the atria and the ventricles is slow or delayed.
What is a grade 3 block?
Third-degree heart block: the heart cannot pump enough blood to the body. This can lead to fainting and shortness of breath. This is an emergency and requires medical attention as soon as possible.
How to differentiate Mobitz 1 and 2?
Mobitz I (Wenckebach sequence): the PR progressively lengthens and at one point a P wave block occurs. Mobitz II: a P wave block occurs occasionally, but with no change in the PR.
How is first-degree AV block cured?
First-degree AV block usually does not require treatment. . Generally, if third-degree AV block is present, an artificial pacemaker should be implanted. In an emergency, a temporary pacemaker is used until a permanent one is implanted.
What is a Mobitz 2 lock?
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz II Second-degree atrioventricular block, Mobitz II type, is less frequent and almost always means severe disease of the conduction system 3. It differs from second-degree AV block type I by presenting constant PR intervals, before and after the blocked P wave.
What consequences does a blockade bring?
Blocking and/or filtering does not guarantee the elimination of content or any type of illegal activity, on the contrary, its content and uses can be replicated on other platforms and can even be «deceived» through techniques or access to tools available on the web .
How long does a block last?
This typically lasts for a few weeks or months, or even permanently in some cases.
How is Mobitz I grade 2 AV block determined?
Mobitz Type I Second-Degree Atrioventricular Block The PR interval is progressively prolonged with each beat until an atrial impulse is not conducted and the QRS complex disappears (Wenckebach phenomenon); AV conduction resumes with the next beat and the sequence repeats.
How to identify branch blocks?
A bundle branch block will appear on the ECG tracing. The tracing of the electrical signal recorded by the electrocardiograph can even indicate whether the blockade is in the right or left branch of the bundle of His.
What causes a first-degree AV block?
(AV block) The most common cause is fibrosis and idiopathic sclerosis of the conduction system. The diagnosis is based on the ECG; symptoms and treatment depend on the degree of blockage, but treatment, if deemed necessary, usually requires a pacemaker.
What causes first-degree AV block?
A first-degree heart block can be caused by the following: Aging. Heart damage from surgery. Muscle damage from a heart attack or other heart muscle problem.
What causes an AV block?
AV block or atrioventricular block is a condition in which electricity is not transmitted well within the heart. The heart is an organ whose function is to pump blood to the rest of the body. For this, it basically consists of muscles capable of contracting by sending blood to the body.
What causes a first-degree AV block?
(AV block) The most common cause is fibrosis and idiopathic sclerosis of the conduction system. The diagnosis is based on the ECG; symptoms and treatment depend on the degree of blockage, but treatment, if deemed necessary, usually requires a pacemaker.
What does a first-degree AV block look like?
In first-degree AV block, conduction is slower, but beats are not skipped. All normal P waves are followed by QRS complexes, but the PR interval is longer than normal (>0.2 seconds).
What consequences does a blockade bring?
Blocking and/or filtering does not guarantee the elimination of content or any type of illegal activity, on the contrary, its content and uses can be replicated on other platforms and can even be «deceived» through techniques or access to tools available on the web .
How long does a block last?
This typically lasts for a few weeks or months, or even permanently in some cases.
How severe is a left bundle branch block?
Left bundle branch block is also associated with an increased risk of death after a heart attack. Some people can have a left bundle branch block for many years without any problems.
What is an advanced lock?
What is a positive lock?
Optimistic locking is a strategy to ensure that the client-side item to be updated (or deleted) is the same as the Amazon DynamoDB item.
How dangerous is a right bundle branch block?
If both the right and left branches are blocked, the main complication is complete obstruction of electrical signaling from the upper to lower chambers of the heart. The lack of signaling can slow the heart rate.
How many rest days after a lockdown?
At the very least, you should rest until you regain feeling in all your extremities, as moving too soon could lead to injury. This usually takes a few hours. If your idea of rest is not doing your normal daily activities, wait at least 24 hours after your epidural.
How long does it take to deflate a nerve?
With rest and other conservative treatments, most people recover from a pinched nerve within a few days or weeks. Surgery is sometimes needed to relieve pain from a pinched nerve.
What is a sciatic nerve injection called?
An epidural steroid injection (ESI) is the delivery of a powerful anti-inflammatory drug directly into the space outside the fluid sac surrounding the spinal cord. This area is called the epidural space.
What do they inject into a lock?
Blocks are done by injecting an anesthetic drug around (or in the plane where the nerves meet) the nerves that carry the sensation of pain to the surgical site (eg, arm, leg, abdomen, chest).